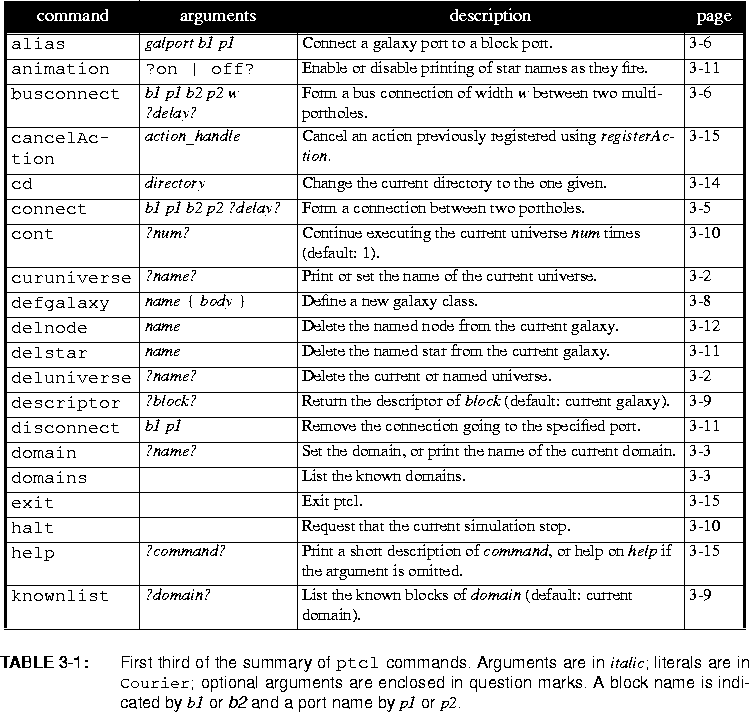








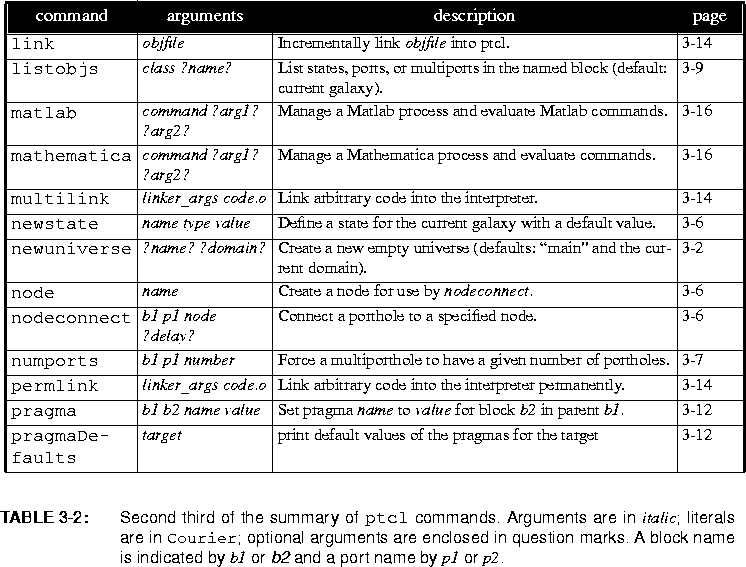
univlistwill return the list of names of universes that currently exist. The command
newuniverse ?name? ?dom?creates a new, empty universe named name (default "main") and makes it the current universe with domain dom (default current domain). If there was previously a universe with this name, it is deleted. Whatever universe was previously the current universe is not affected, unless it was named name. To remove a universe, simply issue the command:
deluniverse ?name?If no argument is given, this will delete the current universe. After this, the current universe will be "main." To find out what the current universe is, issue the command:
curuniverseWith no arguments, this returns the name of the current universe. With one argument, as in:
curuniverse nameit will make the current universe name equal to that argument. A universe can be renamed using either syntax below:
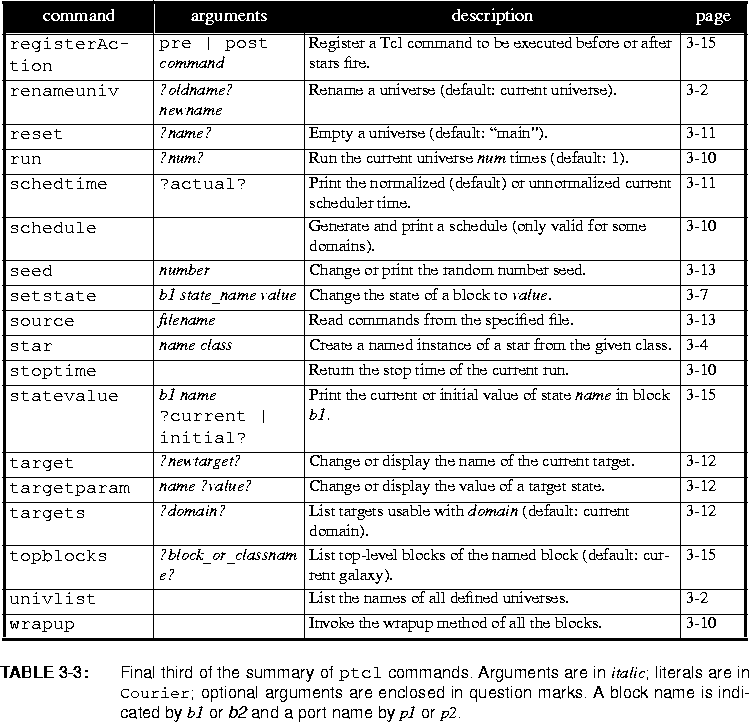
renameuniv newnameWith one argument,
renameuniv oldname newname
renameuniv renames the current universe to newname. With two arguments, it renames the universe named oldname to newname. Note that any existing universe named newname is deleted.SDF. The commanddomain domain-namechanges the current domain; it is only legal when the current galaxy is empty. The argument must be the name of a known domain. The command
domainreturns the current domain. It is possible to create wormholes-interfaces between domains-by including a
domain command inside a galaxy definition. The commanddomainslists the domains that are currently linked into the interpreter.
star name classcreates a new instance of a star or galaxy of class class, names it name, and inserts it into the current galaxy. Any states in the star (or galaxy) are created with their default values. While it is not enforced, the normal naming convention is that name begin with a lower case letter and class begin with an upper case letter (this makes it easy to distinguish instances of a class from the class itself).
connect command. This forms a connection between two stars (or galaxies) by connecting their portholes. A porthole is specified by giving the star (or galaxy) name followed by the port name within the star. The first porthole must be an output porthole and the second must be an input porthole. For example:connect mystar output yourstar inputThe connect command accepts an optional integer delay parameter. For example:
connect mystar output yourstar input 1This specifies one delay on the connection. The delay parameter makes sense only for domains that support it. The delay argument may be an integer expression with variables referring to galaxy parameters as well.
One or both of the portholes may really be a MultiPortHole. If so, the effect of doing the connect is to create a new porthole within the MultiPortHole and connect to that (see also the numports command).
node command creates a node:node nodenameThe
nodeconnect command connects a porthole to a node:nodeconnect starname portname nodename ?delay?Any number of portholes may be connected to a node, but only one of them can be an output node.
busconnect srcstar srcport dststar dstport width ?delay?Here width is an expression specifying the width of the bus (how many portholes in the multiportholes); and delay is an optional expression giving the delay on each connection. The other arguments are identical to those of the
connect command.alias command is used to add a porthole to the current galaxy, and associate it with an input or output porthole of one of the contained stars within the galaxy. An example is:alias galaxyin mystar starinThis also works if starin is a
MultiPortHole (the galaxy will then appear to have a multiporthole as well).newstate command adds a state to the current galaxy. The form of the command isnewstate state-name state-class default-valueThe state-name argument is the name to be given to the state. The state-class argument is the type of state. All standard types are supported (see table 2-6 on page 2-33). The default-value argument is the default value to be given to the state if the user of the galaxy does not change it (using the
setstate command described below). The default-value specifies the initial value of the state, and can be an arbitrary expression involving constant values and other state names; this expression is evaluated when the simulation starts. The following state names are predefined: YES, NO, TRUE, FALSE, PI. YES and TRUE have value 1; NO and FALSE have value 0; PI has the value 3.14159... Some examples are:newstate count int 3The full syntax of state initial value strings depends on the type of state, and is explained in "Parameters and states" on page 2-14.
newstate level float 1.0
newstate title string "This is a title"
newstate myfreq float galaxyfreq
newstate angularFreq float "2*PI*freq"
setstate command is used to change the value of a state. It can be used in three contexts: setstate is:setstate block-name state-name valueHere,
this, which says to change a state belonging to the current galaxy itself.
newstate command. However, the expression for value may refer to the name of one or more states in the current galaxy or an ancestor of the current galaxy.
setstate is given in the section describing defgalaxy below.numports command applies to stars that contain such MultiPortHoles; it causes a specified number of PortHoles to be created within the MultiPortHole. The syntax isnumports star portname nwhere star is the name of a star within the current galaxy, portname is the name of a
MultiPortHole in the star, and n is an integer, representing the number of PortHoles to be created. After the portholes are created, they may be referred to by appending #i, where i is an integer, to the multiporthole name, and enclosing the resulting name in quotes. The main reason for using this command is to allow the portholes to be connected in random order. Here is an example:star summer Add
numports summer input 2
alias galInput summer "input#1"
connect foo output summer "input#2"
defgalaxy command allows the user to define a new class of galaxy. The syntax isdefgalaxy class-name {
command
command
...
}
Here class-name is the name of the galaxy type you are creating. While it is not required, we suggest that you have the name begin with a capital letter in accordance with our standard naming convention - class names begin with capital letters. The command lines may be any of the commands described above - star, connect, busconnect, node, nodeconnect, numports, newstate, setstate, or alias. The defined class is added to the known list, and you can then create instances of it and add them to other galaxies. An example is:resetIn this example, note the use of states to allow the frequency of the sine wave generator to be changed. For example, we could now run the sine generator, changing its frequency to "0.02", with the interpreter input:
domain SDF
defgalaxy SinGen {
domain SDF
# The frequency of the sine wave is a galaxy parameter
newstate freq float "0.05"
# Create a star instance of class "Ramp" named "ramp"
star ramp Ramp
# The ramp advances by 2*pi each sample
setstate ramp step "6.283185307179586"
# Multiply the ramp by a value, setting the frequency
star gain Gain
# The multiplier is set to "freq"
setstate gain gain "freq"
# Finally the sine generator
star sin Sin
connect ramp output gain input
connect gain output sin input
# The output of "sin" becomes the galaxy output
alias output sin output
}
star generator SinGenYou may include a
setstate generator freq "0.02"
star printer Printer
connect generator output printer input
run 100
domain command within a defgalaxy command. If the inside domain is different from the outside domain, this creates an object known as a Wormhole, which is an interface between two domains. An example of this appears in a later section.