

 |  |
|
|
ARCNET COSI libraryThe ARCNET protocol is a token ring protocol. The components that are availalbe in the library are links and nodes at different abstraction levels. The ARCNET library provides two special nodes that are the BUS node (that models an entire ARCNET BUS) and the cross-layer node that models the Medium Access Control, the Physical and the Electrical level. This node is the one used by the synthesis algorithm.ARCNET NodesThe ARCNET library contains the following types of nodes
The base class cosi::library::ArcnetNode is used to derive all other nodes. Figure_arcnetnode shows the different kind of nodes that are modeled by this library. Notice that this figure shows the different abstraction levels but does not specialize the nodes to sensors, actuators etc.
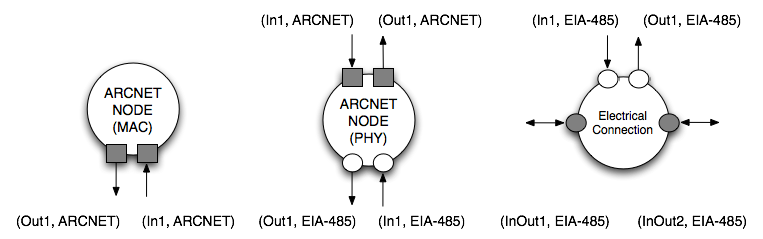
At the medium access control (MAC) level, a nodes has an input and an output interface. These two interfaces are of type ARCNET. The physical layer (PHY) connected to the MAC layer on one side and to actual wires on the other side. The electrical connection is modeled by another node that connects ot the ARCNET physical layer and has two bidirectional ports. This node represents a "T" connection that models the electrical connection in a daisy chain bus. Other electrical connections are possible that possibly have more than two bidirectional ports. ARCNET SensorAn ARCNET sensor is an ARCNET node that sends data of a certain length periodically. The messages back to the MAC layer are the acknowledges that the sensor receives from other nodes. A sensor is characterized by the maximum capacity of its output port.Notice that the capacity limitation is imposed at the PHY layer considering the PHY overhead. ARCNET ActuatorAn ARCNET actuator is an ARCNET node that receives messages with a certain period and sends acknowledges back to the sender. An actuator is characterized by the maximum capacity of its input port.Notice that the capacity limitation is imposed at the PHY layer considering the PHY overhead. ARCNET ControllerAn ARCNET actuator is an ARCNET node that receives data from sensors and sends acknoledges back, and send data to actuators and waits for their acknoledges. In the current status, we do not model any computation on the nodes. An ARCNET controller is characterizes by the maximum output and maximum input capacities.Notice that the capacity limitation is imposed at the PHY layer considering the PHY overhead. ARCNET RouterTBDARCNET LinksThe ARCNET library contains the following types of links
ARCNET BUSA bus can be modeled at different levels of abstractions. At the MAC level, the details of the physical implementation of the bus are abstracted. This model is a good abstraction when:
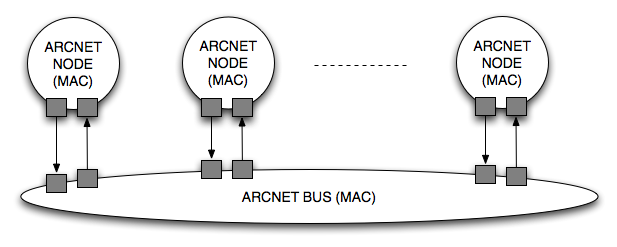
Figure_arcnetbus shows a model of the ARCNET BUS as a node with many input-output port pairs. In this model, an ARCNET BUS has a maximum number of ports and a maximum capacity. The sum of the bandwidth generates by the messages (including the protocol overhead) and the acknoledges must be less than the total bus capacity. When also cost is a concern, then the physical layout of the bus cannot be abstracted. In fact, about half of the cost of a network is in wiring!!! To account for the wiring cost, we need to consider a refined view of an ARCNET BUS shown in Figure_arcnetbusrefinement.
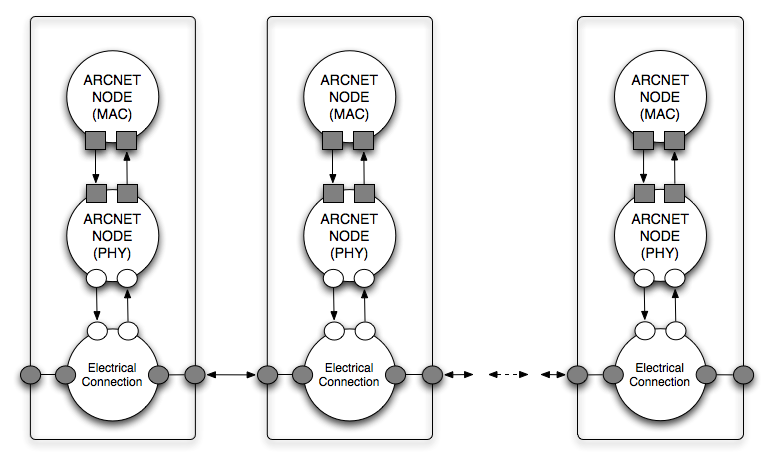
Each actual node is comprised of three layers: MAC, PHY and Electrical. Nodes are connected in daisy chain configuration (this should be enforced by ports and rules). The ARCNET library provides already a cross-layer node that can readly used by a synthesis algorithm. The cross-layer node is an abstraction of all the layers and only exposes the bidirectional electrical interfaces. Each node is labeled with the properties of the MAC and PHY layer. Cost Models Delay Models ARCNET Bus Models Generated on Sun Sep 7 18:37:45 2008 for COSI by  1.5.4 1.5.4
|