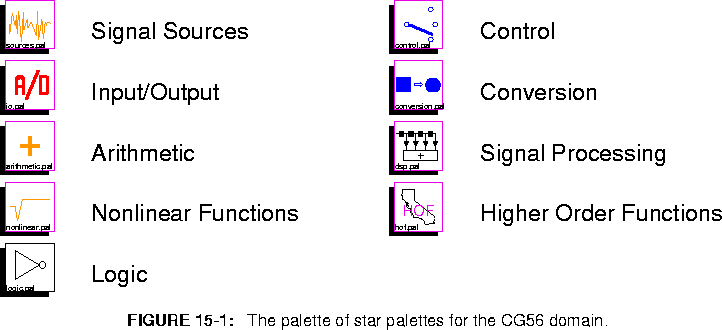







O) will open a checkbox window that you can use to open the standard palettes in all of the installed domains. For the CG56 domain, the star library is large enough that it has been divided into sub-palettes as was done with the SDF main palette.
The top-level palette is shown in figure
15-1. The palettes are Signal Sources, I/O, Arithmetic, Nonlinear Functions, Logic, Control, Conversion, Signal Processing, and Higher Order Functions. The stars on the Higher Order Functions (HOF) palette are used to help lay out schematics graphically. The HOF stars are in the HOF domain, and not the CG56 domain. The names of the others palettes are modeled after the SDF star palettes of the same name in section
5.2 on page 5-4, except the I/O palette which contains target-specific I/O stars for the Ariel S-56X DSP board and the Motorola 56001 simulator. Each palette is summarized in more detail below. More information about each star can be obtained using the on-line "profile" command (,), the on-line man command (M), or by looking in the Star Atlas volume of The Almagest.

BlackHole Discard all inputs. This star is useful for discarding signals that are not useful.
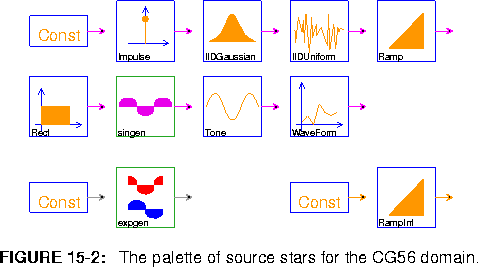
Const, ConstCx, ConstInt, Ramp, RampInt, Rect, singen, and WaveForm.
Impulse Generate a single impulse of size impulseSize (default ONE).
IIDGaussian Generate a white Gaussian pseudo-random process with mean 0 and standard deviation 0.1. A Gaussian distribution is realized by summing noUniforms (default 16) number of uniform random variables. According to the central limit theorem, the sum of N random variables approaches a Gaussian distribution as N approaches infinity.
IIDUniform Generate an i.i.d. uniformly distributed pseudo-random process. Output is uniformly distributed between -range and range (default ONE).
Tone Generate a sine or cosine wave using a second order oscillator. The wave will be of amplitude (default 0.5), frequency (default 0.2), and calcType (default "sin")

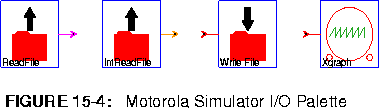
ReadFile Read fixed-point ASCII data from a file. The simulation can be halted on end-of-file, or the file contents can be periodically repeated, or the file contents can be padded with zeros.
IntReadFile Read integer ASCII data from a file. The simulation can be halted on end-of-file, or the file contents can be periodically repeated, or the file contents can be padded with zeros.
WriteFile Write data to a file. The simulator dumps the data presented at the input of this star into a specified file.
Xgraph This star shares the same parameters as its SDF and CGC star equivalents. However, with this star, you can only have one input signal. See
"pxgraph - The Plotting Program" on page 20-1 to learn about plotting options.
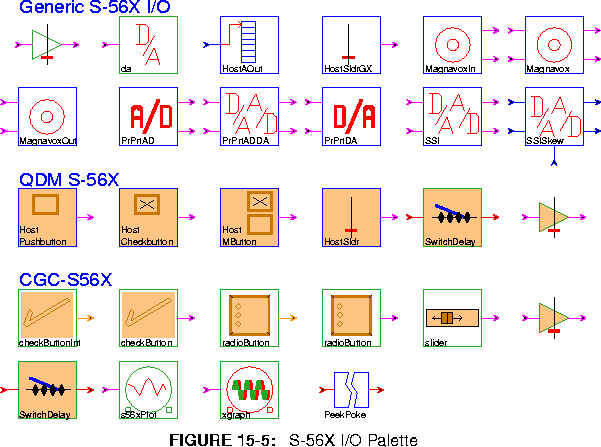
adjustableGainGX Create an interactive adjustable gain using HostSliderGX.
da Send the input to both input ports of the SSI star.
HostAOut Output data from the DSP to host via host port asynchronously.
HostSldrGX Generate an athena widget slider for interactive asynchronous input over the host port.
MagnavoxIn Read data from a Magnavox CD player.
Magnavox Read data from and write data to a Magnavox CD player.
MagnavoxOut Write data to a Magnavox CD player.
PrPrtAD Read from the A/D in Ariel ProPort.
PrPrtADDA Read from the A/D and write to the D/A on the Ariel ProPort.To use both the A/D and D/A on a ProPort you must use this star and not the separate A/D and D/A stars.
PrPrtDA Write to the D/A on the Ariel ProPort.
SSI A generic input/output star for the DSP56001 SSI port.
SSISkew Interface to the 56001 SSI's port with timing-skew capability.
qdmterm_s56x -run.HostButton (2 icons) Graphical two-valued input source. There are two types of buttons: push-buttons and check-buttons. Both present a single button to the user that may be "pressed" with the mouse. The buttons differ in the semantics of the push. When the pushbutton is pressed, the onVal state is output, otherwise offVal.
HostMButton Graphical one-of-many input source. The star always outputs one of a finite number of values: the output is controlled by the user selecting one of several buttons. Exactly one button in the group is on.
HostSldr Graphical host slider for asynchronous input source.
SwitchDelay This galaxy synchronously switches between the input value and the value of the input delayed by TotalDelay (default 8000) samples.
adjustableGain A user adjustable gain, uses HostSlider.
checkButtonInt This galaxy creates a Tk checkbutton widget that produces the given onValue (default 1) when pressed and offValue (default 0) otherwise.
checkButton This galaxy creates a Tk checkbutton widget that produces the given onValue (default 1.0) when pressed and offValue (default 0.0) otherwise.
radioButtonInt This galaxy creates a Tk radiobutton widget that allows the user to select from among a set of possible output values given by pairs (default "One 1" "Two 2").
radioButton This galaxy creates a Tk radiobutton widget that allows the user to select from among a set of possible output values given by pairs (default "One 1" "Two 2")
slider This galaxy creates a Tk slider widget that produces the given value indicated by the slider position which is between low (default 0.0) and high (default 1.0) and initially set to value (default 0.0).
adjustableGain This galaxy multiplies the input by a gain value taken from a Tk slider position between low (default 0.0) and high (default 1.0), which is initially set to value (default 0.0).
SwitchDelay This galaxy synchronously switches between the input value and the value of the input delayed by TotalDelay (default 8000) samples.
s56XPlot This galaxy plots the input interactively using TkPlot.
Xgraph This galaxy simply contains a CGCXgraph star for use in a CG56 galaxy. The galaxy parameters are identical to those of the enclosed star.
PeekPoke Nondeterminate communication link that splices in a peek/poke pair. In this context, it provides a link between the S-56X Motorola 56001 board and the workstation.
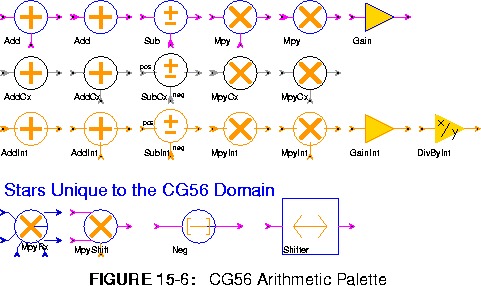
Add (2 icons) Output the sum of the inputs. If saturation is set to yes, the output will saturate.
Sub Outputs the "pos" input minus all of the "neg" inputs.
Mpy (2 icons) Outputs the product of all of the inputs.
Gain The output is set the input multiplied by a gain term. The gain must be in [-1,1).
AddCx (2 icons) Output the complex sum of the inputs. If saturation is set to yes, the output will saturate.
SubCx Outputs the "pos" input minus all of the "neg" inputs.
MpyCx (2 icons) Outputs the product of all of the inputs.
AddInt (2 icons) Output the sum of the inputs. If saturation is set to yes, the output will saturate.
SubInt Outputs the "pos" input minus all of the "neg" inputs.
MpyInt (2 icons) Outputs the product of all of the inputs.
GainInt The output is set the input multiplied by an integer gain term.
DivByInt This is an amplifier. The integer output is the integer input divided by the integer divisor (default 2). Truncated integer division is used.
MpyRx Multiply any number of rectangular complex inputs, producing an output.
MpyShift Multiply and shift.
Neg Output the negation of the input.
Shifter Scale by shifting left leftShifts bits. Negative values of leftShifts implies right shifting.
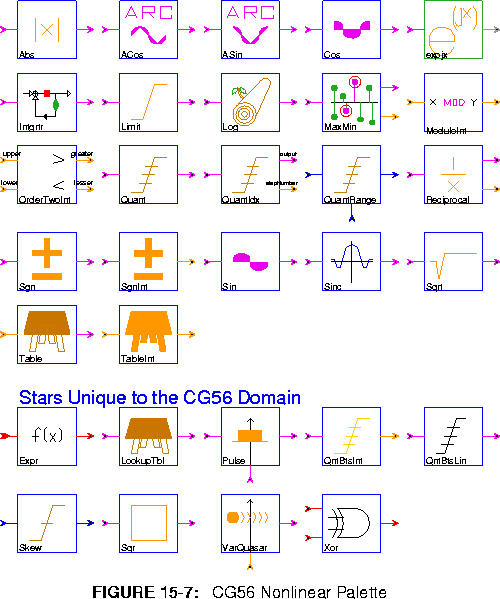
Abs Output the absolute value of the input.
ACos Output the inverse cosine of the input, which is in the range -1.0 to 1.0. The output, in the principle range of 0 to 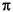 , is scaled down by
, is scaled down by 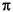 .
.
ASin Output the inverse sine of the input, which is in the range -1.0 to 1.0. The output, in the principle range of 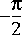
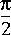
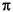 .
.
Cos Output the cosine, calculated the table lookup. The input range is [-1,1] scaled by 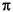 .
.
expjx Output the complex exponential of the input.
Intgrtr An integrator with leakage set by feedbackGain. If there is an overflow, the onOverflow parameter will designate a wrap around, saturate or reset operation.
Limit Limits the input between the range of [bottom, top].
Log Outputs the base two logarithm.
MaxMin Output the maximal or minimal (MAX) sample out of the last N input samples. This can either compareMagnitude or take into account the sign. If outputMagnitude is YES the magnitude of the result is written to the output, otherwise the result itself is written.
ModuloInt Output the remainder after dividing the integer input by the integer modulo parameter.
OrderTwoInt Takes two inputs and outputs the greater and lesser of the two integers.
Quant Quantizes the input to one of N+1 possible output levels using N thresholds.
QuantIdx The star quantizes the input to one of N+1 possible output levels using N thresholds. It also outputs the index of the quantization level used.
QuantRange Quantizes the input to one of N+1 possible output levels using N thresholds.
Reciprocal Outputs the reciprocal to Nf precision in terms of a fraction and some left shifts.
Sgn Outputs the sign of the input.
SgnInt Outputs the sign of the integer input.
Sin Outputs the sine, calculated using a table lookup. The input range is [-1,1) scaled by 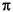 .
.
Sinc Outputs the sinc functions calculated as sin(x)/x.
Sqrt Outputs the square root of the input.
Table Implements a real-valued lookup table. The values state contains the values to output; its first element is element zero. An error occurs if an out of bounds value is received.
TableInt Implements an integer-valued lookup table. The values state contains the values to output; its first element is element zero. An error occurs if an out of bounds value is received.
Expr General expression evaluation.
LookupTbl The input accesses a lookup table. The interpolation parameter determines the output for input values between table-entry points. If interpolation is "linear" the star will interpolate between table entries; if interpolation is set to "none", it will use the next lowest entry.
Pulse Generates a variable length pulse. A pulse begins when a non-zero trigger is received. The pulse duration varies between 1 and maxDuration as the control varies between [-1,1).
QntBtsInt Outputs the two's complement number given by the top noBits of the input (for integer output).
QntBtsLin Outputs the two's complement number given by the top noBits of the input, but an optional offset can be added to shift the output levels up or down.
Skew Generic skewing star.
Sqr Outputs the square of the input.
VarQuasar A sequence of values(data) is repeated at the output with period N (integer input), zero-padding or truncating the sequence to N if necessary. A value of O for N yields an aperiodic sequence.
Xor Output the bit-wise exclusive-or of the inputs.
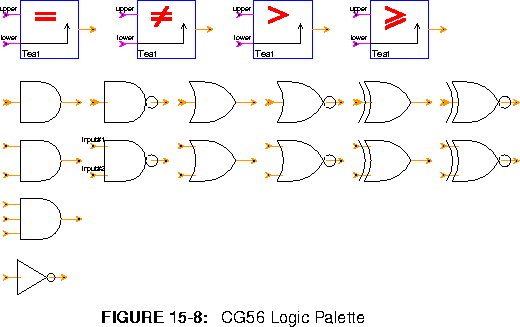
Test (4 icons) Test to see if two inputs are equal, not equal, greater than, and greater than or equal. For less than and less than or equal, switch the order of the inputs.
And (3 icons) True if all inputs are non-zero.
Nand (2 icons) True if all inputs are not non-zero.
Or (2 icons) True if any input is non-zero.
Nor (2 icons) True if any input is zero.
Xor (2 icons) True if an odd number of inputs is non-zero.
Xnor (2 icons) True if an even number of inputs is not non-zero.
Not Logical inverter.

Fork, DownSample, Commutator, Distributor, Mux, Repeat, Reverse, and UpSample.
ChopVarOffset This star has the same functionality as the Chop star except now the offset parameter is determined at run time through a control input.
Cut On each execution, this star reads a block of nread samples (default 128) and writes nwrite of these samples (default 64), skipping the first offset samples (default 0). It is an error if nwrite + offset > nread. If nwrite > nread, then the output consists of overlapping windows, and hence offset must be negative.
Delay A delay star of parameter totalDelay unit delays.
Pad On each execution, Pad reads a block of nread samples and writes a block of nwrite samples. The first offset samples have value fill, the next nread output samples have values taken from the inputs, and the last nwrite - nread - offset samples have value fill again.
Rotate The star reads in an input block of a certain length and performs a circular shift of the input. If the rotation is positive, the input is shifted to the left so that ouput[0] = input[rotation]. If the rotation is negative, the input is shifted to the right so that output[rotation] = input[0].
sampleNholdGalaxy
This sample-and-hold galaxy is more memory efficient than using a downsample star for the same purpose.
VarDelay A variable delay that will vary between 0 and maxDelay as the control input varies between -1.0 and 1.0.
WasteCycles Stalls the flow of data for cyclesToWaste number of cycles.
CxToRect Output the real part and imaginary part of the input of separate output ports.
RectToCx Output a complex signal with real and imaginary part inputs.
BitsToInt Convert a stream of bits to an integer.
IntToBits Convert an integer into a stream of bits.
FixToCx Convert fixed-point numbers to complex fixed-point numbers.
FixToInt Convert fixed-point numbers to complex fixed-point numbers.
CxToFix Convert fixed-point numbers to complex fixed-point numbers.
CxToInt Convert fixed-point numbers to complex fixed-point numbers.
IntToFix Convert fixed-point numbers to complex fixed-point numbers.
IntToCx Convert fixed-point numbers to complex fixed-point numbers.
Goertzel and IIR stars are identical to their SDF counterparts.
Allpass An allpass filter with one pole and one zero. The location of these is given by the "polezero" input.
Biquad A two-pole, two-zero IIR filter (a biquad).
Comb A comb filter with a one-pole lowpass filter in the delay loop.
BiquadDSPlay A two-pole, two zero IIR filter (a biquad). This biquad is tailored to use the coefficients from the DSPlay filter design tool. If DSPlay gives the coefficients: A B C D E then define the parameters as follows: a=A, b=B, c=C, d=-(D+1), e = -E. This only works if a, b, c, d, and e, are in the range [-1,1). The default coefficients implement a low pass filter.
FIR A finite impulse response (FIR) filter. Coefficients are specified by the taps parameter. The default coefficients give an 8th order, linear-phase, lowpass filter. To read coefficients from a file, replace the default coefficients with < filename, preferably specifying a complete path. Polyphase multirate filtering is also supported.
LMS An adaptive filter using the LMS adaptation algorithm. The initial coefficients are given by the coef parameter. The default initial coefficients give an 8th order, linear phase lowpass filter. To read default coefficients from a file, replace the default coefficients with < filename, preferably specifying a complete path. This star supports decimation, but not interpolation.
LMSGanged A LMS filter were the coefficients from the adaptive filter are used to run a FIR filter in parallel. The initial coefficients default to a lowpass filter of order 8.
LMSRx A Complex LMS filter
RaisedCos An FIR filter with a magnitude frequency response shaped like the standard raised cosine used in digital communications. See the SDFRaisedCosine star for more information.
GoertzelDetector, GoertzelPower, and LMSOscDet are identical to their SDF counterparts.FFTCx Compute the discrete-time Fourier transform of a complex input using the fast Fourier transform (FFT) algorithm. The parameter order (default 8) is the transform size. The parameter direction (default 1) is 1 for forward, -1 for the inverse FFT.
Window Generate standard window functions or periodic repetitions of standard window functions. The possible functions are Rectangle, Bartlett, Hanning, Hamming, Blackman, SteepBlackman, and Kaiser. One period of samples is produced on each firing.