





The Higher Order Function stars are accessed through the main palette of the domains that support HOF. For example, the HOF stars are a sub-palette of the SDF star palette since the SDF domain supports HOF. The top-level palette for the HOF domain is shown in figure 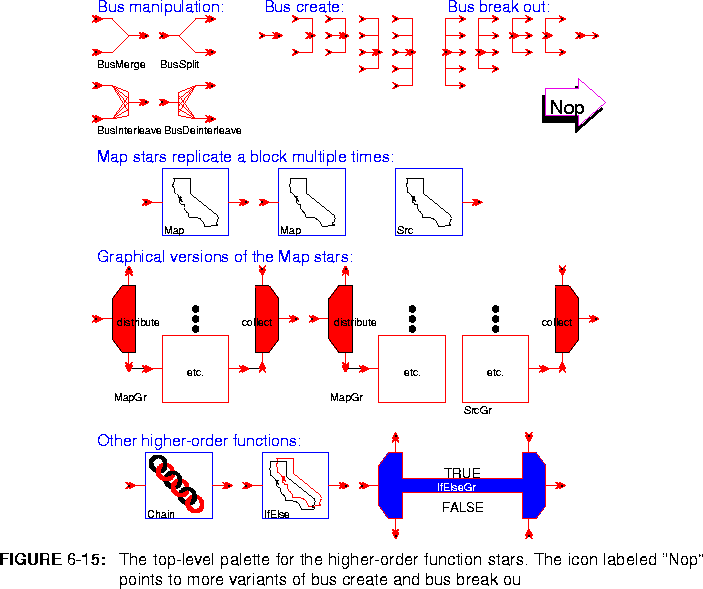 6-15.
6-15.
The top group in the main HOF palette are the bus manipulation stars, summarized below:
BusMerge Bridge inputs to outputs and then self-destruct. This star merges two input busses into a single bus. If the input bus widths are M1 and M2, and the output bus width is N, then we require that N = M1 + M2. The first M1 outputs come from the first input bus, while the next M2 outputs come from the second input bus.
BusSplit Bridge inputs to outputs and then self-destruct. This star splits an input bus into two. If the input bus width is N, and the output bus widths are M1 and M2, then we require that N = M1 + M2. The first M1 inputs go the first output bus, while the next M2 inputs go to the second output bus.
BusInterleave Bridge inputs to outputs and then self-destruct. This star interleaves two input busses onto a single bus. The two input busses must have the same width, which must be half the width of the output bus. The input signals are connected to the output in an alternating fashion.
BusDeinterleave Bridge inputs to outputs and then self-destruct. This star deinterleaves a bus, producing two output busses of equal width. The input bus must have even width. The even numbered input signals are connected to the first output bus, while the odd numbered input signals are connected to the second output bus.
Nop Bridge inputs to outputs and then self-destruct. This star is used to split a bus into individual lines or combine individual lines into a bus. It is also used to break out multi-inputs and multi-outputs into individual ports. These icons are labeled "BusCreate" and "BusSplit", suggesting their usual function.
If you look inside the icon labeled "Nop" to the right of the above stars, you will open another palette with more icons for the Nop stars, shown in figure
6-16.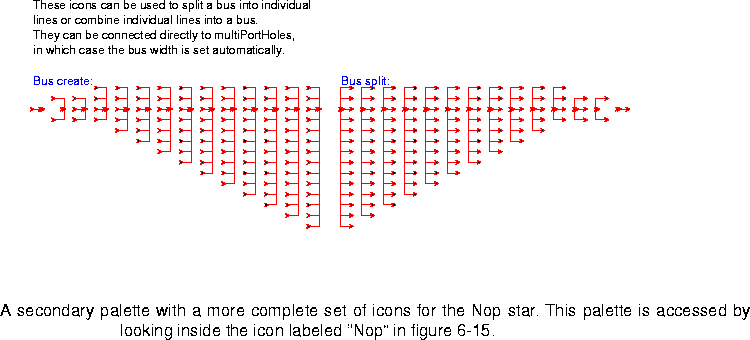
Map (Two icons.) Map one or more instances of the named block to the input stream(s) to produce the output stream(s). This is implemented by replacing the Map star with one or more instances of the named block at preinitialization time. The replacement block(s) are connected as specified by input_map and output_map, using the existing connections to the Map star. Their parameters are determined by parameter_map. See
"Setting parameter values" on page 6-6 for examples of the use of parameter_map.
Src This is identical to the Map star, except that the replacement block is a source block (it has no inputs).
MapGr A variant of the Map star where the replacement block is specified by graphically connecting it. There must be exactly one block connected in the position of the replacement block. The Nop stars are the only exception: they may be used in addition to the one replacement block in order to control the order of connection.
SrcGr This is identical to the MapGr star, except that the replacement block is a source block (it has no inputs)
Chain Create one or more instances of the named block connected in a chain. This is implemented by replacing the Chain star with instances of the named blocks at preinitialization time. The replacement block(s) are connected as specified by input_map, internal_map, and output_map. Their parameters are determined by parameter_map. If pipeline is YES, then a unit delay is put on all internal connections.
IfElse This star is just like Map, except that it chooses one of two named blocks to replace itself. If the condition parameter is TRUE, then the true_block is used. Otherwise, the false_block is used. This can be used to parameterize the use of a given block, or, more interestingly, for statically evaluated recursion.
IfElseGr A variant of the IfElse star where the two possible replacement blocks are specified graphically rather than textually. There must be exactly one block connected in the position of each of the two the replacement blocks. The Nop stars are the only exception: they may be used in addition to the two replacement blocks in order to control the order of connection. As of this writing, this star cannot be used with recursion, because pigi will attempt to compile the sub-galaxy before it can be deleted from the schematic by IfElseGr.







Copyright © 1990-1997, University of California. All rights
reserved.